symptoms of a bad power valve 2 stroke

In a 2-stroke engine, the power valve is a crucial component that plays a pivotal role in controlling exhaust port timing that leads to engine performance. When a power valve becomes faulty or not working properly, it can lead to a range of issues. These include issues around the engine’s power output, fuel efficiency, and overall engine performance. Let’s learn further about the symptoms of a bad power valve 2 stroke below.
What is a power valve 2 stroke?
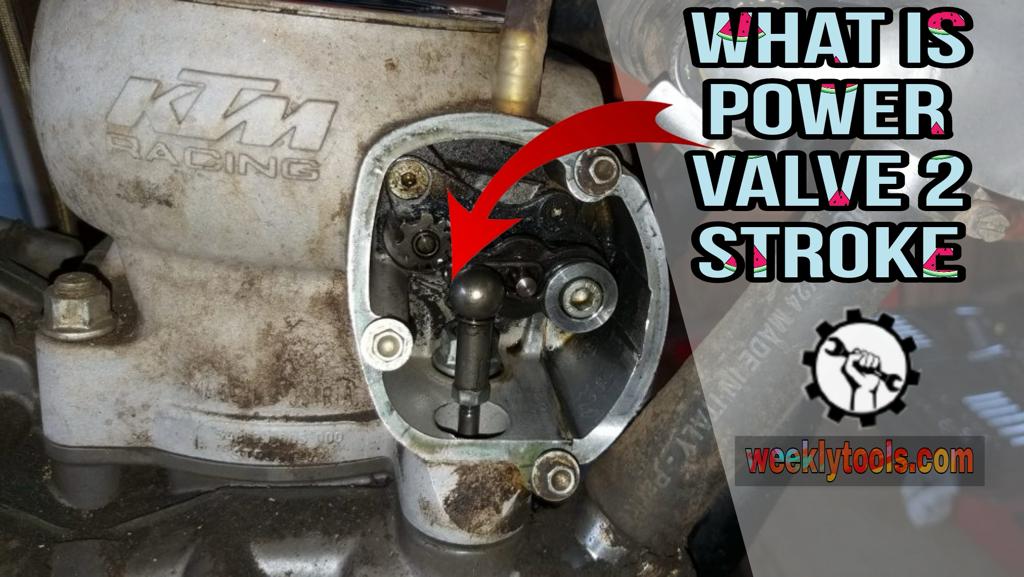
A power valve 2 stroke is a metal component located within the exhaust port of the two-stroke engine. Its primary function is to regulate the size of the exhaust port during engine operation, thus controlling the power output across various RPM ranges. By adjusting the size of the exhaust port, the power valve allows for more precise tuning of the engine’s performance characteristics. It plays a pivotal role in broadening the engine’s power band, enabling it to produce power at different ranges of RPMs.
Symptoms of a Bad Power Valve in a 2-Stroke Engine

A malfunctioning power valve can lead to a range of symptoms that impact the engine’s performance. You might barely notice the signs at first but they will surely develop into a more serious problem when left untreated. The symptoms can be challenging to detect without a proper understanding of the power valve’s function and its influence on the engine. However, they’re driven by two conditions: low power valve value and high power valve value.
Low Power Valve Value Condition
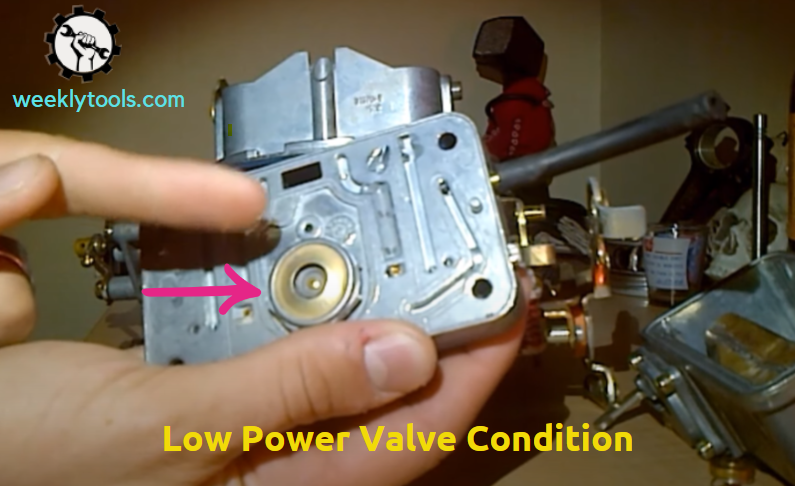
1) Poor Acceleration
When the power valve opens later than expected, it leads to a significant decrease in acceleration performance. This phenomenon can be attributed to the role of the exhaust system, particularly the muffler and catalytic converter. In the normal state(fully functioning engine), these components work in tandem to reduce noise and minimize exhaust emissions.
However, if they become clogged or malfunction, the engine’s effectiveness diminishes, causing sluggishly poor acceleration. The reduced airflow due to a delayed power valve opening worsens the problem, making the engine feel underpowered, especially during quick accelerations.
2) Backfires When Accelerating
Backfiring is another noticeable sign of a malfunctioning power valve in the 2-stroke engine. This occurs when the engine’s internal combustion process is disrupted. In simple terms, it means that the spark plugs may fail to ignite the air-fuel mixture at the right time. The result is a poor ignition process, leading to backfires.
These backfiring issues can occur if the spark fires prematurely, before the intake valves close, or after the exhaust valves open. An overly rich air-fuel mixture that prevents the fuel from burning completely before the exhaust valve opens can also cause this issue. This chaotic combustion process can create loud and potentially damaging backfires.
3) Air/Fuel Mixture Too Lean
When the engine experiences a lean air/fuel mixture, it’s a sign that there is an imbalance in the combustion process. In this scenario, there is not enough fuel in the combustion chamber, which ignites with an excessive amount of air. A lean air/fuel mixture is often an indicator of broader issues within the engine, such as a faulty fuel pump, damaged fuel injectors, or a malfunctioning oxygen sensor.
Obviously, the consequence of this lean mixture is a reduction in power at specific RPMs. Furthermore, it can lead to difficulties in engine starting, as the engine lacks the necessary power to turn the crankshaft effectively. These symptoms together paint a clear picture of a power valve that is not performing optimally.
High Power Valve Value Condition

1) Rough Idling
When the power valve opens too early in the RPM range, it results in rough idling. This phenomenon is characterized by unpredictable RPM fluctuations and vibrations, making it easily noticeable. The severity of rough idling can vary depending on the engine’s temperature and the specific components involved.
Possible causes for rough idling may include clogged or faulty components within the ignition or emission systems. A clogged expansion chamber or leak detection pump can disrupt the engine’s operation, causing a rough idle.
Additionally, a loose, cracked, or damaged vacuum hose can lead to air leakage, further exacerbating the problem. Moreover, a dirty Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) valve may permit excess air into the engine, resulting in increased oil consumption and rough idling.
2) Reduced Gas Mileage
The premature opening of the power valve can have a significant impact on the engine’s fuel consumption. Increased fuel consumption is often associated with a malfunctioning Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) valve. When the EGR valve fails to function properly, it can cause fuel to burn at suboptimal temperatures, reducing fuel efficiency.
You may detect this issue through the smell of unburned fuel from the exhaust tailpipe or the appearance of increased soot during acceleration. A similar problem can occur if the catalytic converter becomes clogged or damaged, hindering the efficient flow of exhaust gases and causing excessive fuel consumption.
3)Black Smoke in the Exhaust
Black smoke emanating from the exhaust is a clear indicator that the engine is burning an excess amount of fuel. This could signify issues like fuel contamination or an excessive mixture of fuel with engine oil. However, black smoke can also be generated by a blocked manifold, a clogged air filter, or malfunctioning fuel injectors.
Additionally, a defective catalytic converter can result in the engine burning too much oil or becoming clogged with coolant fluid. This obstruction hinders the effective passage of exhaust gases, ultimately leading to the emission of black smoke. This symptom serves as a visual and olfactory cue to a power valve that requires attention.
How to Fix a Bad Power Valve (30 words)
Fixing a bad power valve in a 2-stroke engine involves inspecting the valve itself, cleaning it to remove carbon buildup, and ensuring it operates smoothly. You can also adjust the tension on the valve’s spring to fine-tune its performance.
Conclusion
The power valve is a critical component in a 2-stroke engine, and when it malfunctions, it can lead to a range of performance issues. Understanding the symptoms of a bad power valve is essential for timely diagnosis and maintenance to keep your engine running at its best. Regular inspections and proper maintenance are key to preventing power valve problems and ensuring the optimal performance of your 2-stroke engine.

As a mechanical engineer, it’s easy for David to explain the functionality of the tool. David test most of the tools before writing a review. its help him to learn something new and suggest the best product for you.





